A Super Alternative to Traditional Conditioners: Plant-Based Biostimulants--Aliginate Oligosaccharides
Seaweed is the most important part of marine plants, and it has a wide variety of species and is widely distributed, generally including brown algae, red algae, green algae and cyanobacteria. Seaweed is rich in bioactive molecules, such as alginate, seaweed polysaccharide, algal starch, etc., which have antibacterial, antiviral, antioxidant and other biological activities. It is a natural plant nutrition conditioner and an ideal fertilizer additive.
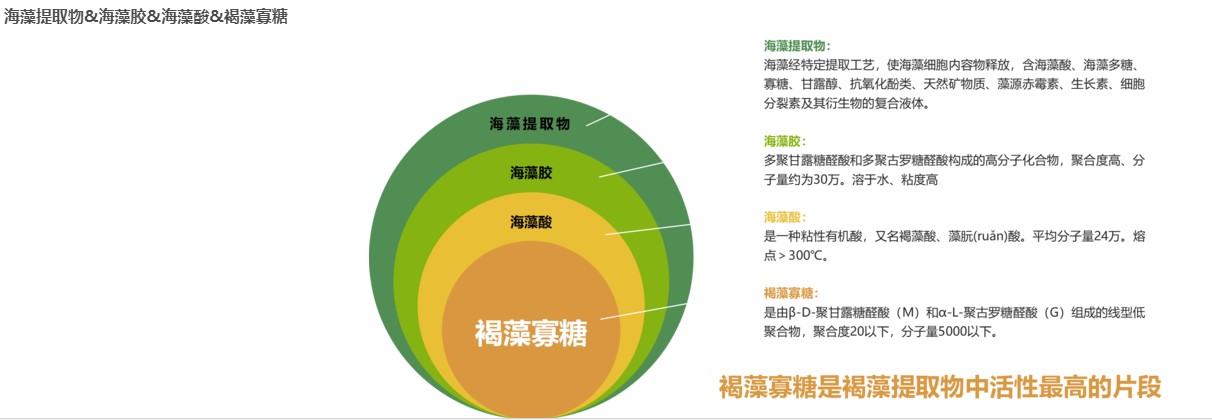
Seaweed polysaccharide is a kind of multi-component mixture, which is a high-molecular carbohydrate composed of multiple identical or different monosaccharide groups connected by glycosidic bonds. It has anti-virus, anti-tumor, anti-mutation, anti-radiation and immunity enhancement. effect. However, seaweed polysaccharides often have the characteristics of large molecular weight, high viscosity and low solubility, which affect their application in the fields of biomedicine and agriculture.
Seaweed oligosaccharide is a linear or branched compound with a degree of polymerization of 2 to 10 obtained from the degradation of seaweed polysaccharide. It retains unique active groups, and has the advantages of small molecular weight and good water solubility. It has attracted more and more attention. Seaweed oligosaccharides are represented by brown seaweed oligosaccharides.
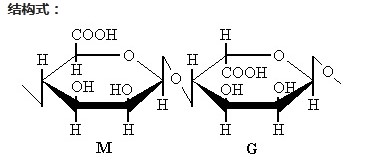
Aliginate oligosaccharide is a linear oligosaccharide composed of β-D mannuronic acid and α-L guluronic acid connected by β-1-4 glycosidic bonds. It is a functional oligosaccharide and is more beneficial to agricultural fertilizers. Add other applications. Qingdao Sapphire's algal oligosaccharide uses the oligomer of alginate from Ascophyllum nodosum from Northern Ireland, which has the physical and chemical properties of low molecular weight, strong water solubility, high stability, safety and non-toxicity. Agricultural grade brown algae oligosaccharide is a plant-derived phytostimulant, also known as plant vaccine. It has low molecular weight, good water solubility, good compatibility, and has a wide range of biological activity advantages. It is a natural plant nutrition regulator and an ideal fertilizer additive. , has broad application prospects in agricultural production.
Agricultural grade algin oligosaccharides can be used as signal molecules to participate in the regulation of plant growth and development, breaking seed dormancy and promoting germination and root growth. The main mechanisms are as follows:
1. Promote crop growth
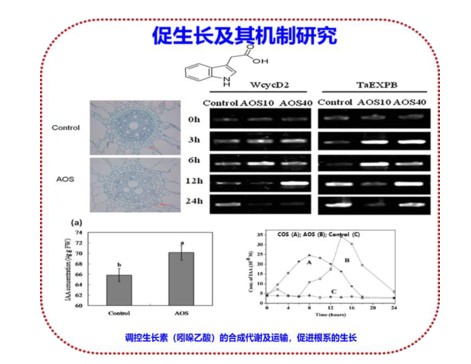
The study found that fucoidan oligosaccharides can induce the production of callus, significantly enhance the content of hormones (indole acetic acid, etc.) in cells, and stimulate the expression of auxin-related genes by promoting the content of hormones, lipase, amylase and protease. Promote seed germination and seedling growth and rooting.
2. Enhance crop resistance
As a plant endogenous oligosaccharide, brown algae oligosaccharide acts as a signal molecule in plant stress resistance. Fucoid oligosaccharide will form a protective film, which can effectively protect protein molecules from inactivation and inactivation, so as to maintain the life process and biological characteristics of living organisms, thus showing extraordinary resistance to external harsh environments.
Abscisic acid is a very important growth hormone in plants and plays an important role in coping with adversity stress. The application of fucoidan oligosaccharide can induce and increase the secretion of plant growth hormones such as abscisic acid in plants. The research results show that algae oligosaccharide can induce the accumulation of abscisic acid in plants, reaching 5-7 times the normal level, and has a significant anti-stress effect.
3. Inhibit plant pathogens
As an elicitor, algal oligosaccharide induces disease resistance in plants. Alginic acid oligosaccharide can significantly reduce the yellowing of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves caused by pathogen infection, the content of the important disease resistance regulatory hormone salicylic acid and the expression of the signaling pathway marker disease resistance gene PR1 are significantly increased, and the salicylic acid signal The pathway is involved in the process of alginate oligosaccharide-induced resistance to bacterial diseases in Arabidopsis.



 Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510
Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510 Phone (Fax):86-53283197178
Phone (Fax):86-53283197178 E-mail:
E-mail:  Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400
Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400

