What is the role of the trace element boron in plant growth?
Discovered in 1923 as an essential trace element, boron is found in soil and is also mined for industrial use.
How does boron work for plant growth?
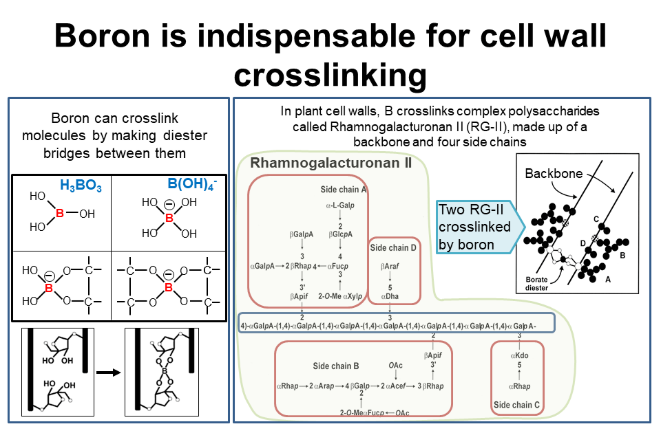
Boron is indispensable for cell wall cross-linking, and it can cross-link molecules by creating diester bridges between them.
I. Role and efficacy of boron Fertilizer
1. Boron can promote the transport of carbohydrates and metabolic processes, when the plant body contains the appropriate amount of boron, can improve the supply of organic matter in the various organs of the crop, improve the crop's rate of fruitfulness and the rate of fruiting.
2. Boron plays an important role in the growth and elongation of the root system of the crop, which is due to the fact that boron can play a role in promoting cell elongation and cell division in the crop.
3. Boron has a facilitating effect on the fertilisation process, because the amount of boron in pollen, with the stigma and ovary containing the most, can stimulate the germination of pollen and the elongation of pollen tubes, so that pollination can be carried out smoothly, thus improving the success rate of pollination. If there is a lack of boron fertilizer, it is easy to see the phenomenon of crops flowering but not fruiting.
4. Boron in the plant body can regulate the formation and operation of organic acids, when the crop is deficient in boron, organic acids will be accumulated in large quantities in the root, resulting in inhibition of cell differentiation and elongation of the apical meristematic tissues, the occurrence of corky, thus causing root necrosis.
5. Boron can enhance the crop's ability to resist adversity, and promote early maturity of crops.
6. Boron can improve the legume crops rhizobium nitrogen fixation ability, but also can promote the crop on the absorption of calcium.
II. Manifestations of boron deficiency in plants
The growing point at the top of the plant develops abnormally or stops growing, the young leaves show deformity, crumpling, and irregular fading of green between the veins, and the old leaves in its lower part become thicker and dark blue or dark green in colour; the leaves and stems become brittle, and with the further development of boron deficiency, the growing point at the top of the plant will die, and the whole plant seems to look shorter and shorter.



 Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510
Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510 Phone (Fax):86-53283197178
Phone (Fax):86-53283197178 E-mail: admin@bluealga.com
E-mail: admin@bluealga.com Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400
Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400

