Spirulina-Algae with Mysterious Power【2】
↓
In the previous article we will continue to talk about the value of spirulina.
Nutritional value of Spirulina
Spirulina has a high protein content, contains a special pigment protein - phycocyanin, radicicin and vitamins, and contains essential large amounts of elements and trace elements.
Spirulina is highly valued by scientists and international organizations around the world for its comprehensive and balanced nutrition and its high value in disease prevention and health care. Nutritionists and pharmacologists call it "the nutritional champion of the earth" and "the new star of medicinal source". The World Health Organization has recognized spirulina as "the best health product of the 21st century" and "the super nutritious food of the future"; UNESCO has recommended spirulina as "the most ideal and perfect food of tomorrow"; the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) has also solemnly approved spirulina as "the most ideal and perfect food of tomorrow "The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations also solemnly recommends Spirulina to the world as "the best food resource and future food for human beings".
The nutritional value of spirulina is considered by modern science to be a "miniature nutritional reservoir", with the content of eight essential amino acids close to or exceeding that of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The ratio of protein, sugar and fat is about 60:20:5, which is a balanced nutritional composition. In addition, it also contains a variety of vitamins and trace elements, including β-carotene content of 4000mg/kg, vitamins up to 1320mg/kg, each person daily consumption of 15g dry weight spirulina can ensure the necessary source of nutrients. Spirulina is regarded as "the most ideal and best food for human beings" by FAO for its high nutrition and safety.
The food value of Spirulina
CCTV.com has published a related article, which mentions: from the perspective of biochemical composition, spirulina does have its special features. It has a high protein content, up to 70% of the dry weight, and the amino acid composition of the protein is also close to the human body needs; in its fat, the proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids is high; its vitamin content, especially the B vitamins, vitamins C, D, E and carotenoids, and mineral content is also relatively rich. In addition, it contains a relatively large amount of pigments. Because all these ingredients are meaningful for human nutrition, people do have high hopes for it and it is not too much to say that it is an excellent food.
Spirulina has been consumed by humans for a long time. Commercial farming is mainly used for making health products, producing high-grade aquafeeds, and extracting cyanobacterial protein. A variety of food products have been developed using Spirulina, all of which are made by adding dried Spirulina powder or extract to conventional foods or beverages, each with its own characteristics. The main products reported are soy sauce, yogurt, jelly, beverages and noodles.
Chemical composition of Spirulina
The chemical composition of spirulina is characterized by high protein, low fat and low sugar, and contains a variety of vitamins and trace elements, which has a high nutritional value.
The protein content of spirulina is as high as 60%-70%, which is 2 times that of soybeans, 3.5 times that of beef and 4 times that of eggs, and it contains a complete range of essential amino acids with a reasonable composition.
The fat content of spirulina is generally 5%-6% of the dry weight, of which 70%-80% is unsaturated fatty acids (UFA), especially the content of linolenic acid up to 500 times that of human milk.
Spirulina cellulose content is 2%-4%, and the cell wall is mainly composed of collagen The cell wall is mainly composed of collagen and hemicellulose, and its absorption rate by human body is over 95%.
Spirulina is also extremely rich in vitamins and minerals, the former including vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, E and K; the latter including zinc, iron, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, iodine and other trace elements, the ratio of bio-zinc to iron in spirulina is basically the same as the human physiological needs and is most easily absorbed by the body.
In addition, the phycocyanin in Spirulina phycocyanin (CPC), phycocyanin algal polysaccharide (PSP), andγ-linolenic acid methyl ester (GLAME), β-carotene chlorophyll a The active ingredients such as PSP, γ-linolenic acid methyl ester (GLAME), β-carotene and chlorophyll a have regulatory effects on many animal functions.
Scientific value of Spirulina
1. For medical research
Spirulina is low in fatty acids, of which unsaturated fatty acids, which are very beneficial to the human body, account for a large proportion. Spirulina is rich in many bioactive components, such as beta-carotene, algae bile protein spirulinaγ-linolenic acid and endogenous enzymes, which are very beneficial to human health.
2. Used as a feed additive
Spirulina is now widely used as a feed additive in animal feeds due to its rich protein and amino acid content and rich in many trace elements. Some researchers have reported the application of this new green feed additive in aquaculture and livestock production. Studies have shown that the addition of 4% of Spirulina-Orchidium concentrate powder can improve South American white shrimp growth performance. Spirulina has been reported to improve piglets production performance of piglets.
3. Use as bioenergy
As early as the 1970s, due to the oil crisis, the concern for clean, non-polluting and renewable bioenergy has become a hot spot, especially the preparation of biohydrogen energy. Many countries have invested a lot of human and material resources in the research of bio-hydrogen production technology and accumulated a lot of research results. It has been found that Spirulina has the characteristics of high photosynthesis efficiency, fast growth and reproduction, high hydrogenase activity and long continuous hydrogen release compared with other bio-hydrogen producing materials, which is one of the ideal materials for studying bio-hydrogen release.
4. For environmental protection
Spirulina needs to absorb and consume nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus in the water environment as well as degrade organic matter in the water during the growth and reproduction process, and has the characteristics of fast growth and reproduction, high light efficiency and high adaptability. These characteristics of Spirulina suggest that using wastewater to culture Spirulina can, on the one hand, purify the water body and reduce the eutrophication of the water body; on the other hand, it can also obtain high value-added Spirulina products. Thus the use of Spirulina for wastewater treatment is a good biological pollution control measure.
5. Use as agricultural fertilizer
Spirulina contains a large amount of protein and a variety of vitamins and mineral elements, the unique growth factor can better promote plant growth, after multi-layer wall-breaking crushing, fermentation, biological enzymatic digestion and other complex processes, to obtain easy to be absorbed by plants, high activity of natural amino acid composition. Spirulina extract is used in the crop cultivation industry to receive unexpected miraculous results.
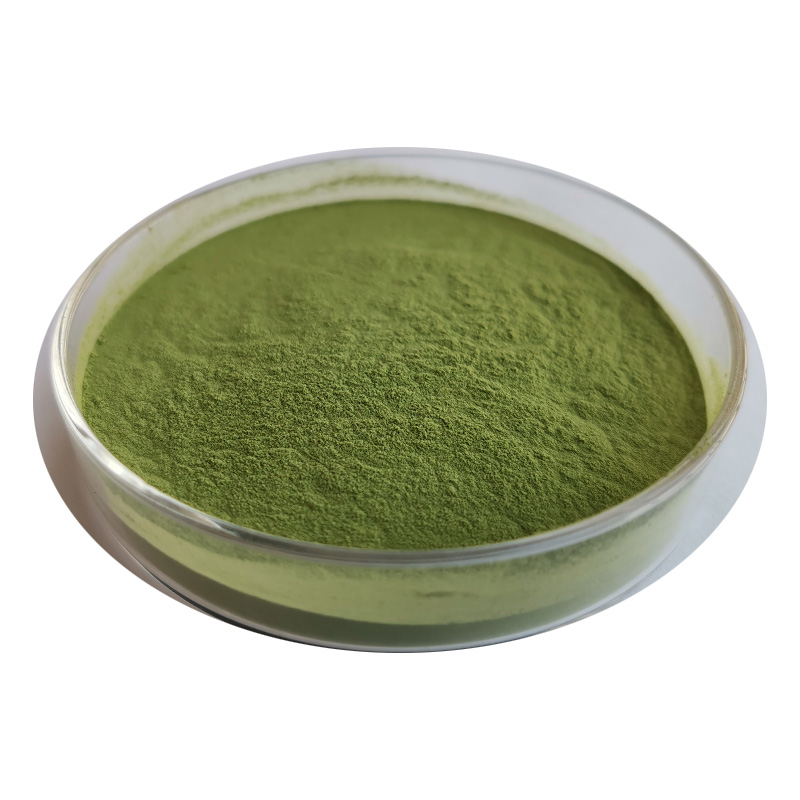

BlueAlga Spirulina extract Efficacy:
Enhance plant photosynthesis, flower and fruit preservation, improve fruit set rate improve immunity to improve quality and increase yield;
Promote the development of plant root system, accelerate plant growth and reproduction;
Promote crops with natural immunity and resistance to adversity, crops will be more robust, fruit or vegetable quality to be naturally enhanced;
Promote healthy plant growth with deep roots, green leaves, strong stems and sweet fruits, not only to improve yields, but also to promote the return of the product to its natural healthy form.



 Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510
Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510 Phone (Fax):86-53283197178
Phone (Fax):86-53283197178 E-mail:
E-mail:  Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400
Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400

